Biologics in Severe Asthma: How Anti-IgE and Anti-IL-5 Therapies Work
 Dec, 1 2025
Dec, 1 2025
When inhalers aren’t enough
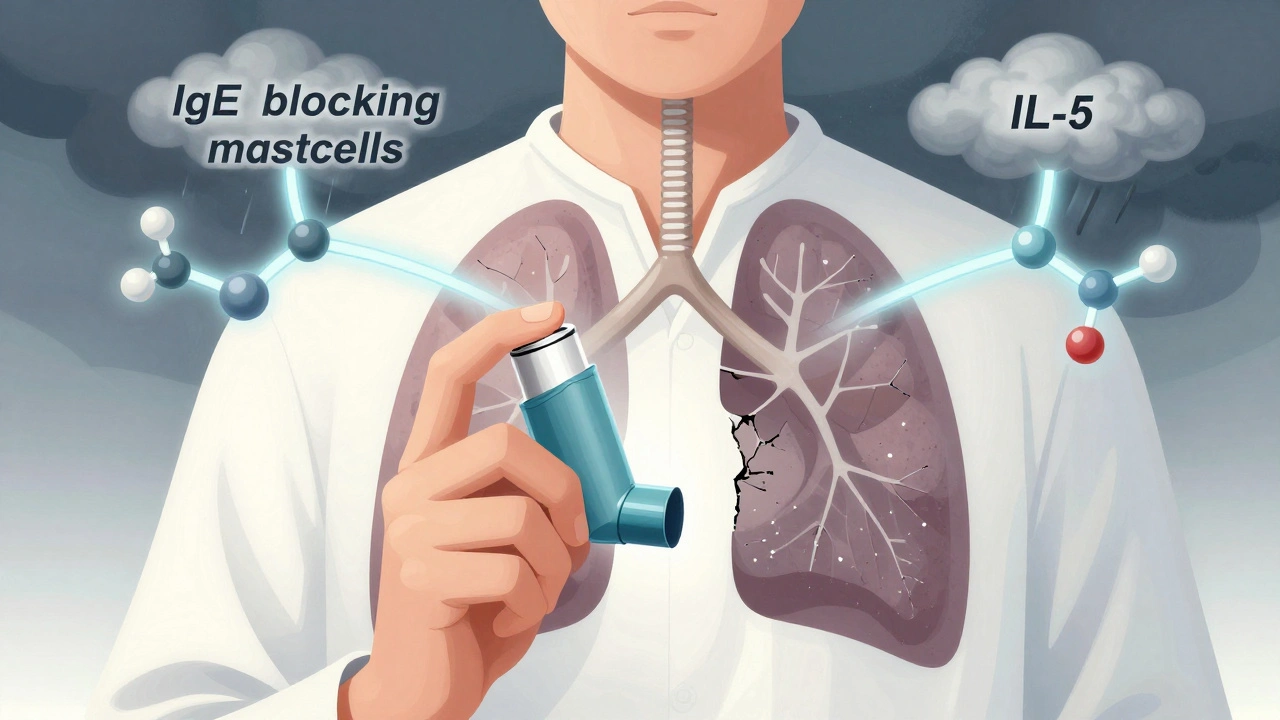
For people with severe asthma, standard treatments like inhalers and oral steroids often fall short. Even with daily use, they might still wake up gasping, end up in the ER, or rely on monthly steroid bursts just to stay stable. That’s where biologics come in. These aren’t your typical pills or sprays-they’re precision drugs made from living cells, designed to shut down specific parts of the immune system driving asthma flare-ups. Two of the most established types target anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 pathways. They don’t cure asthma, but for the right patients, they can turn a life of constant fear into one with real breathing room.
What is anti-IgE therapy?
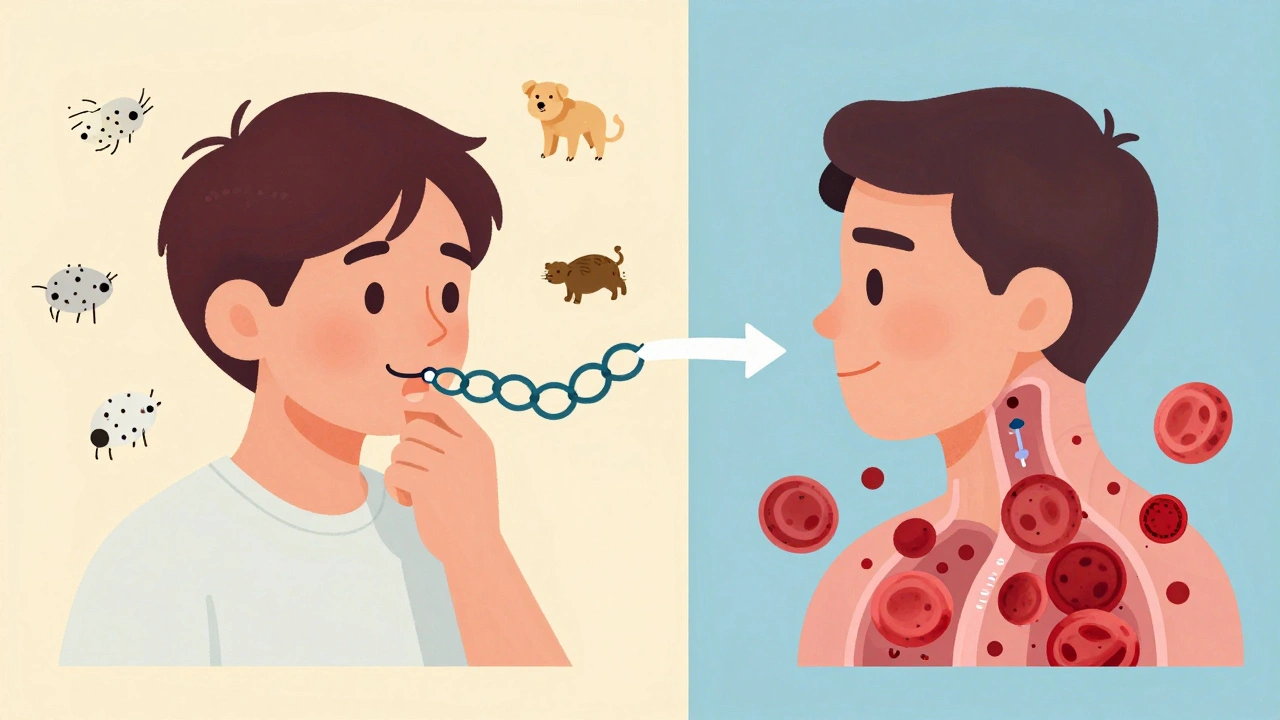
Omalizumab (brand name Xolair) was the first biologic approved for asthma back in 2003. It works by latching onto IgE, the antibody that triggers allergic reactions. In allergic asthma, IgE binds to mast cells and basophils, causing them to dump histamine and other inflammatory chemicals into the airways. Omalizumab blocks that binding, preventing the chain reaction before it starts.
This therapy is only for people with confirmed allergic asthma. You need to test positive for at least one perennial allergen-like dust mites, pet dander, or cockroach proteins-and have serum IgE levels between 30 and 1500 IU/mL. It’s not for everyone with asthma, only those whose symptoms are tied to allergies. Studies show it cuts asthma attacks by about 50% in the right group. The INNOVATE trial found patients had fewer ER visits, fewer hospital stays, and needed less oral steroids after starting treatment.
Dosing is based on your weight and IgE level. Most people get an injection every 2 to 4 weeks. It’s given under the skin, often with an auto-injector pen. Side effects are usually mild: headache, sore throat, or a red, itchy spot at the injection site. But there’s a small risk-about 1 in 1,000 doses-of a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. That’s why you’re asked to wait 30 minutes after your first few doses.
What is anti-IL-5 therapy?
While anti-IgE targets allergies, anti-IL-5 therapies go after a different problem: eosinophils. These are white blood cells that swell up in the airways of some asthma patients, causing chronic inflammation. High levels mean more flare-ups, more damage, and more reliance on steroids.
Three drugs fall under this category: mepolizumab (Nucala), reslizumab (Cinqair), and benralizumab (Fasenra). Mepolizumab and reslizumab bind directly to IL-5, the signal that tells eosinophils to multiply. Benralizumab goes one step further-it binds to the IL-5 receptor on the eosinophils themselves, tricking the immune system into killing them off. This is called antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, or ADCC. Within 24 hours of a benralizumab shot, blood eosinophil counts can drop by over 95%.
To qualify, you need to have eosinophilic asthma. That means your blood eosinophil count has been 150 cells/μL or higher in the past year, or 300 cells/μL or higher. Your doctor will check this with a simple blood test. These drugs aren’t meant for non-eosinophilic asthma. If your eosinophils are low, they won’t work.
Benefits are strong: mepolizumab reduced exacerbations by 52% in the MENSA trial. Benralizumab cut them by 51% in the ZONDA trial. Many patients report fewer hospitalizations and can cut or stop oral steroids entirely. Reslizumab is the only one given as an IV infusion-every 4 weeks-which means you have to go to a clinic. The others are self-injected at home.

How do they compare?
Choosing between anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 isn’t about which is “better.” It’s about which matches your asthma type.
| Feature | Anti-IgE (Omalizumab) | Anti-IL-5 (Mepolizumab, Benralizumab) |
|---|---|---|
| Target | IgE antibody | IL-5 or IL-5 receptor |
| Best for | Allergic (atopic) asthma | Eosinophilic asthma |
| Required biomarker | Serum IgE (30-1500 IU/mL) | Blood eosinophils ≥150-300 cells/μL |
| Dosing frequency | Every 2-4 weeks | Every 4 weeks (mepolizumab); every 8 weeks after 3 doses (benralizumab) |
| Administration | Subcutaneous injection | Subcutaneous (mepolizumab, benralizumab); IV infusion (reslizumab) |
| Speed of eosinophil reduction | No direct effect | Benralizumab: 24 hours; mepolizumab: weeks |
| Reduction in exacerbations | ~50% | 51-52% |
| Oral steroid reduction | Yes, in many | Yes, often more pronounced |
One key difference: benralizumab doesn’t just block IL-5-it kills eosinophils fast. That’s why some patients see results quicker. But if you have both allergies and high eosinophils, your doctor might consider both pathways. Tezepelumab (Tezspire), approved in 2021, is newer and targets TSLP, an upstream signal that drives multiple inflammation types, even in non-eosinophilic asthma. It’s an option if you don’t fit neatly into either category.
Who qualifies-and who doesn’t
Biologics aren’t first-line. Before even thinking about them, your doctor needs to confirm you’re doing everything right with standard care. That means:
- Your inhaler technique is perfect (many patients think they’re using them right, but they’re not)
- You’re taking your meds consistently
- You’ve ruled out triggers like smoking, uncontrolled allergies, or GERD
- You’ve tried high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting beta agonist
If you’ve done all that and still have 2 or more flare-ups a year, or need oral steroids more than twice in 12 months, you might be a candidate. But not everyone responds. Real-world data shows 30-40% of patients don’t get meaningful improvement. That’s why biomarkers are critical. If your IgE is too low or your eosinophils are normal, the drug won’t work-no matter how bad your asthma feels.
Cost, access, and daily reality
These drugs cost between $25,000 and $40,000 a year in the U.S. Insurance rarely covers them without prior authorization, which can take 2-3 weeks. Even then, you might need to try cheaper options first. In New Zealand and other countries with public healthcare, access is tighter-only patients with the most severe, uncontrolled asthma get approved.
Most patients learn to self-inject after 2-3 supervised sessions. The pens are simple, but anxiety about needles is common. Some report mild pain or bruising at the injection site, especially at first. But for many, the trade-off is worth it. One Reddit user, u/AsthmaWarrior2020, said after six months on mepolizumab, his ER visits dropped from 3-4 a year to zero. He stopped daily prednisone.
But it’s not perfect for everyone. Another user, u/BreathlessInSeattle, had to quit benralizumab after three doses because of severe joint pain. Side effects like this are rare but real. The risk of anaphylaxis is low, but you need to know the signs: swelling, trouble breathing, dizziness. Always carry an epinephrine auto-injector if your doctor recommends it.
What to expect over time
Don’t expect instant results. Some people feel better in 4 weeks. Others take 12-16 weeks. Patience is key. Your doctor will track your asthma control with tools like the Asthma Control Test and monitor your blood eosinophils or IgE levels every few months.
Many patients see big improvements in quality of life. A 2023 survey found 78% of users felt more in control of their asthma, and 65% were able to reduce or stop oral steroids. That’s huge-because long-term steroid use can cause weight gain, bone loss, diabetes, and mood changes.
But biologics aren’t a cure. You still need your inhalers. You still need to avoid triggers. You still need to see your specialist. They’re powerful tools, but they work best as part of a full plan-not a replacement for good asthma management.
The future of asthma treatment
The field is moving fast. New biologics are in development, including ones you’d only need twice a year. Researchers are also testing combinations-like pairing anti-IgE with anti-IL-5-to see if hitting multiple pathways works better. AI tools are being built to predict who will respond based on blood markers, lung function, and even genetic data.
For now, the message is clear: if you have severe asthma that’s not under control, talk to your allergist or pulmonologist about biologics. Don’t assume you’re out of options. For the right person, these drugs can mean the difference between living with asthma and living beyond it.

Grant Hurley
December 1, 2025 AT 16:37Just started mepolizumab last month and honestly? My ER visits dropped from 4 to 0 in 6 weeks. I still use my inhaler, but I’m sleeping through the night for the first time in years. No more prednisone hangovers either. Worth every penny if your docs actually listen.
Shannon Gabrielle
December 3, 2025 AT 04:19Oh great another $40k miracle drug for people who can’t follow basic instructions. You know what fixes asthma? Quit smoking. Stop breathing in cat dander. Use your inhaler right. But no, let’s inject biologics and call it science. Classic American healthcare.
Lucinda Bresnehan
December 3, 2025 AT 06:44I’m a nurse who’s seen this firsthand. One patient, 72, on benralizumab-stopped needing steroids, started gardening again. But the real win? She finally stopped feeling like a burden. These drugs don’t just treat asthma, they restore dignity. Even if insurance fights you, keep pushing. You deserve to breathe.
Conor Forde
December 4, 2025 AT 08:54Anti-IgE? More like Anti-Common-Sense. You mean to tell me we’re spending 40 grand a year to block a molecule… when the real issue is that half the population lives in moldy apartments and the other half thinks ‘asthma’ means ‘I forgot my inhaler’? This is like putting a Band-Aid on a leaking dam and calling it innovation. Also-why is reslizumab the only one that requires a clinic visit? Because Big Pharma loves making people commute. 🙄
patrick sui
December 5, 2025 AT 02:59Hey all-just want to say if you’re considering biologics, don’t skip the biomarker testing. I had ‘severe asthma’ for 12 years, tried everything, then found out my eosinophils were normal. Turns out I had silent GERD + bad inhaler technique. Once I fixed those? No biologic needed. But if you’ve done the work and still struggle? You’re not broken-you’re just not the right fit for the old tools. Keep asking questions. 🤝
Nnaemeka Kingsley
December 6, 2025 AT 13:13From Nigeria here-my cousin in Lagos uses omalizumab. It’s not easy to get, but her church helped fund it. She used to miss school every month. Now she’s studying engineering. These drugs change lives even where healthcare is broken. Don’t give up.
Declan O Reilly
December 8, 2025 AT 11:09There’s something poetic about this, isn’t it? We’ve spent centuries treating asthma as if it were just a cough or a wheeze. But now we’re learning it’s a whisper from the immune system screaming for help. Anti-IgE and anti-IL-5 aren’t just drugs-they’re translations. We’re finally learning to listen. And for the first time, some of us can breathe without fear. That’s not medicine. That’s poetry made real.
Kshitij Shah
December 9, 2025 AT 03:47Bro in India here. My uncle’s on Xolair. Costs more than his monthly salary. Insurance? Nah. So he gets it through a pharma charity program. He still uses his inhaler, still avoids dust, still hates needles. But he walks his granddaughter to school now. That’s the real ROI. No stats needed.
Sean McCarthy
December 10, 2025 AT 15:24According to the NIH, 30-40% of patients don’t respond. According to the FDA, efficacy is measured by exacerbation reduction. According to insurance companies, cost is the only metric that matters. According to patients? We’re tired. We’re not numbers. We’re not data points. We’re people who can’t sleep. We’re people who need more than a pill. We need a system that doesn’t treat us like a liability.
ANN JACOBS
December 11, 2025 AT 01:15As someone who has personally navigated the labyrinthine bureaucracy of biologic insurance approvals-often requiring three prior authorizations, two appeals, and a signed letter from a pulmonologist affirming that I am, in fact, breathing poorly-I must say: the emotional toll of this process is as debilitating as the disease itself. The fact that a life-altering therapy can be withheld for weeks due to administrative delays, while patients suffer preventable hospitalizations, is not merely a systemic flaw-it is a moral failure of the highest order. That said, I am grateful for the progress we’ve made, and I remain hopeful that future iterations of this system will prioritize human dignity over actuarial tables.